
Deemerwha studio/Shutterstock
By Abhinav Lal/
Arduino libraries, like libraries for other programming languages, help easily extend the range of functions available to users in the standard integrated development environment (IDE). They are commonly used to interface with hardware (such as a display or sensor) or for adding code functionality (data processing or storage). While you could potentially code (in Arduino programming language, or C/C++) the required functions from scratch yourself, using an already available library lets you integrate commonly features without spending time and effort.
Libraries installed via Library Manager are located within the Sketchbook folder, called Arduino by default and located at C:UsersusernameDocumentsArduino on Windows, /Users/username/Documents/Arduino on macOS, and /home/username/Arduino on Linux. You can check your Sketchbook folder location via the Arduino IDE: go to «Sketchbook location» in File > Preferences on Windows and Linux, and Android IDE > Preferences on macOS. In legacy versions of the IDE (v2.1 or older), Preferences is called Settings.
Within the Sketchbook folder, you’ll find a folder named «libraries». It is here you will find library folders, named after the respective libraries. It is within the specific library folder you can find useful things like Examples and the Readme file. If you’re manually installing a library from a ZIP file, without using the Add .ZIP Library option in the IDE’s Library Manager, then this is where you should place the extracted contents of the ZIP file — specifically, the main folder named after the library and all its subfolders. Refer to the Installing Libraries documentation for more details.
Different types of Arduino libraries
Boopathi Kumar/Shutterstock
A point to note is that while Arduino libraries can be found within the IDE installation folder, the Sketchbook folder, and the core folder, it is only the libraries within the Sketchbook folder that are used during compilation. Also note that libraries included in board packages themselves are found in a different location — the board package folder’s libraries subfolder. Refer to Arduino’s documentation to see where that’s listed.
There are a variety of libraries available to Arduino microcontroller users, from those select few included as standard Arduino libraries in the Library Manager of the Arduino IDE, to a wider list of official libraries, as well as the vast variety of contributed libraries that have been developed by the community and approved for release by the company. Arduino uses the following categorisation for libraries — Communication, Data Processing, Data Storage, Device Control, Display, Other, Sensors, Signal Input/Output, and Timing — with additional categories such as Audio, Connectivity, Cryptography, Memory, and Robotics. Libraries are also available for different Arduino microcontroller and component architectures, such as AVR or ESP8266.
Where can you find Arduino libraries to install?
SlashGear
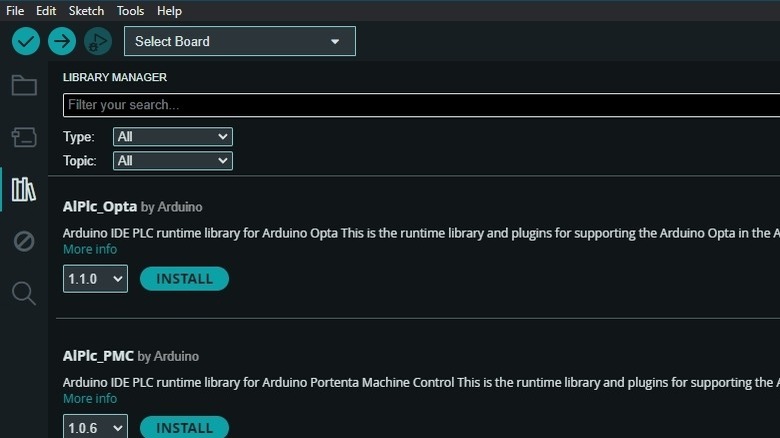
The standard Arduino libraries (common for beginner Arduino projects) as well as wide list of contributed libraries can be found within the Arduino IDE itself. In Arduino IDE 1 (specifically v1.6.2 onwards), you will need to visit the Library Manager, via Sketch > Include Library. Here, you can select from listed libraries, import a ZIP library via the Add .ZIP Library option, or, click the Manage Libraries… option, which opens the Library Manager. Here you can search libraries via Type and Topic, and once you find the one you want, select the version and click on Install.
In Arduino IDE 2, you will need to click on the Library icon on the left pane, and this directly takes you to the Library Manager page, which lets you search for libraries or browse through a list of popular libraries. Otherwise, you could follow the same steps as IDE 1, and visit Sketch > Include Library, where you will get the options of Manage Libraries… and Add .ZIP Library. In both Arduino IDE 1 and 2, the Manage Libraries… option is also available in the Tools menu.
Finally, you can also manually download its ZIP file from a webpage, and then import it or manually place it in the appropriate folder. You can find libraries on the official Arduino Libraries page, the Libraries for Arduino page in Arduino Playground, or via an open-source library index, via GitHub, via the PlatformIO library page, or finally, via another GitHub repository.